
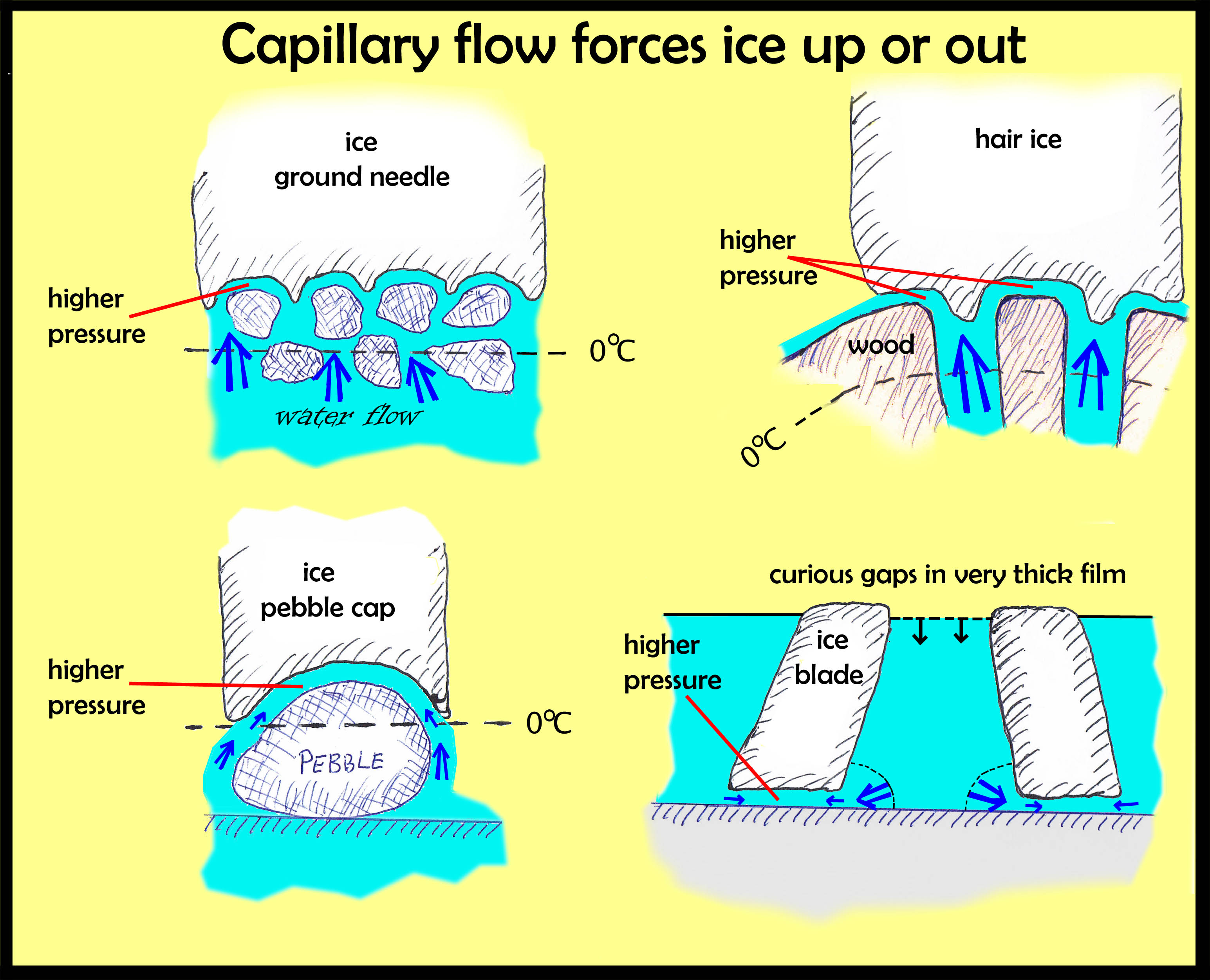
How capillary action and the meniscus are related to intermolecular forces in water.
Twist a couple of pieces of paper towel together until it forms something that looks a little like a piece of rope, this will be the ‘wick’ that will absorb and transfer the water (a bit like the wick on a candle transferring the wax to the flame).

Key concepts Plant biology Capillary action Water Dyes Colors Introduction Have you ever heard someone say, “That plant is thirsty,” or “Give that plant a drink of water.”?
Cohesion (from Latin cohaesiō “cling” or “unity”) or cohesive attraction or cohesive force is the action or property of like molecules sticking together, being mutually attractive.It is an intrinsic property of a substance that is caused by the shape and structure of its molecules, which makes the distribution of orbiting electrons irregular when molecules …
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (µm) in diameter, and having a wall one endothelial cell thick. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: they convey blood between the arterioles and venules.These microvessels are the site of exchange of many substances with the interstitial fluid surrounding them. Substances which exit include water …


Glossary of Water Resource Terms. A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z A abandoned water right a water right which was not put to beneficial use for a


502.2-2 volatile organic compounds in water by purge and trap capillary column gas chromatography with photoionization and electrolytic conductivity detectors in …

EPA Method 524.3 in the EPA methods list database. View all EPA methods
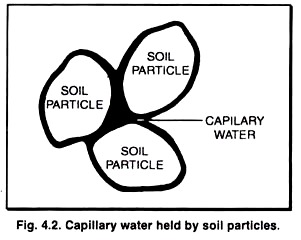
Capillarity: Capillarity, rise or depression of a liquid in a small passage such as a tube of small cross-sectional area, like the spaces between the fibres of a towel or the openings in a porous material. Capillarity is not limited to the vertical direction. Water is drawn into the fibres of a towel, no matter

The viscosity of Newtonian fluids can be most precisely determined using capillary viscometers. This method of measurement, measures the time taken for a defined quantity of fluid to flow through a capillary with a known diameter and known length.